DART (Direct Analysis in Real Time) is a new ion source that can analyze
samples with various states and shapes without any sample preparation.
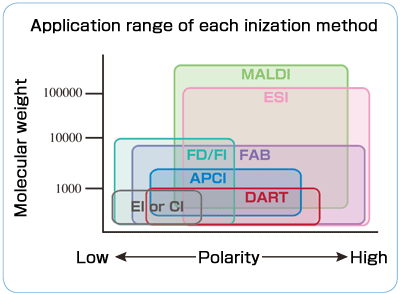
JEOL, the pioneer of ambient ionization
DART was born in 2003 at the mass
spectrometry applications laboratory of JEOL USA, Inc. Among a series of new
ionization techniques, which were later termed “ambient ionization,” DART was
the first to have been invented and the first to have been commercialized in
2005. It was introduced at the Pittsburgh Conference in February 2005 and
awarded the Pittcon Editor’s Gold Award as one of the best new products of the
year. It was also awarded for the R&D 100 Award in September of the same
year.
Direct analysis without sample preparation
You can acquire high mass-resolution, accurate-mass spectra in real time by simply presenting samples
of various shapes and states to the DART ion source without any sample
preparation. DART can handle samples with arbitrary shapes or “dirty” sample
that conventional analytical method cannot deal with.
|
Subjects for analysis
|
Paper (bills, business cards, etc.), film, textiles, fruits, vegetables, spices, beverages, biofluids, human skin, glass, concrete, etc.
|
Detectable
components
|
Drugs and their metabolites, synthetic chemicals, dyes, pigments, pesticide, odor components, narcotics, designer drugs, chemical warfare agents and related substances, explosives, etc.
|
Direct analysis of liquid
Direct analysis of solid
Direct analysis of powder
AccuTOF LC-plus 4G + DART: the perfect combination
The DART was developed for the JEOL AccuTOF series of mass spectrometers.
No additional interface is required between the DART and the AccuTOF LC-plus 4G
due to a rugged, simple API interface and high-capacity vacuum pumping system.
The combination is able to detect a wider range of polar and nonpolar compounds
than any other DART MS system. With no additional interface, there is virtually
no carryover from one analysis to another, even for “dirty” and “sticky”
samples.
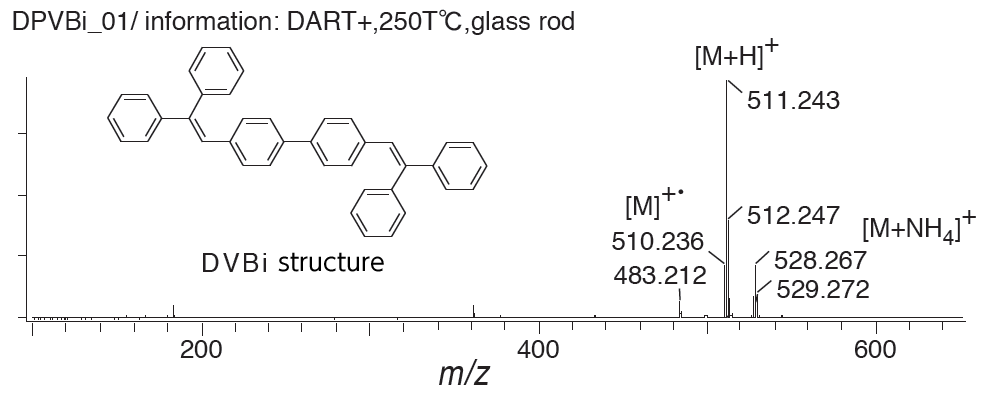
Nonpolar: organic electro-luminescence materials
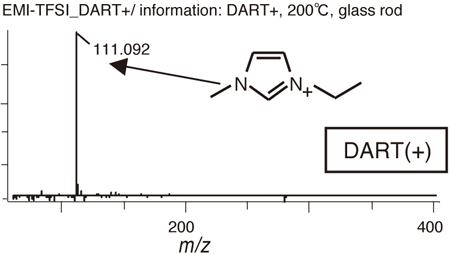
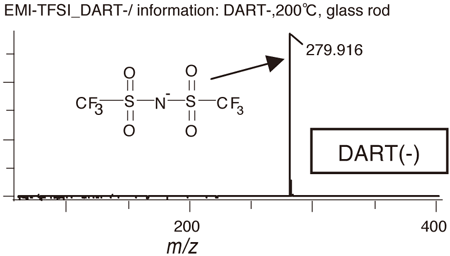
Polar: an ionic liquid
Principle of DART ionization
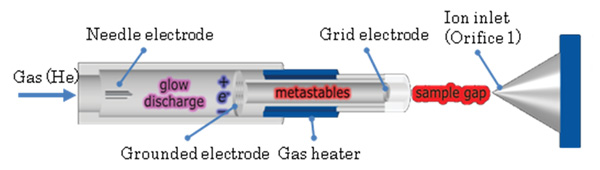
DART ionization is based on the interaction between excited state atoms or
molecules, and atmospheric gas and/or analytes.
Plasma is generated by glow discharge from the needle electrode in a helium
gas stream. The plasma includes ions, electrons, and excited state (metastable)
atoms or molecules. The majority of charged particles are eliminated by the
grounded electrode and the excited state neutral species are expelled to the
atmosphere.
The gas stream can be heated by the gas heater to help analytes
vaporization or desorption from the substrate surface.
Positive ion
The metastable helium atoms formed in the DART source react with
atmospheric water to produce ionized water clusters. These protonated water
clusters can then react with the analyte (M) to form protonated cations:
He(23S) + H2O → H2O+. + He(11S) + e-
H2O+. + H2O → H3O+ + OH.
H3O+ + nH2O → [(H2O)n+1 + H]+
[(H2O)n+1 + H]+ + M → [M + H]+ + (n+1)H2O
Negative ion
Metastable helium atoms can react with a neutral (N), such as the exit grid
electrode, or another neutral species to form electrons through Penning
ionization. The electrons formed are rapidly thermalized by collisions with
atmospheric gases (G) and then react with gaseous oxygen to produce oxygen
anions.
He(23S) + N → N+. + He(11S) + e-*
e-* + G → G* + e-
e- + O2 → O2-
These oxygen anions can then react with sample molecules (M) to produce
analyte anions.
O2-. + M → [M - H]- + OOH.
O2-. + M → M-. + O2
O2-. + M → [M + O2]-.
Direct analysis of liquid
Direct analysis of solid
Direct analysis of powder
AccuTOF LC-plus 4G + DART: the perfect combination
The DART was developed for the JEOL AccuTOF series of mass spectrometers.
No additional interface is required between the DART and the AccuTOF LC-plus 4G
due to a rugged, simple API interface and high-capacity vacuum pumping system.
The combination is able to detect a wider range of polar and nonpolar compounds
than any other DART MS system. With no additional interface, there is virtually
no carryover from one analysis to another, even for “dirty” and “sticky”
samples.
Nonpolar: organic electro-luminescence materials

Polar: an ionic liquid


Principle of DART ionization

DART ionization is based on the interaction between excited state atoms or
molecules, and atmospheric gas and/or analytes.
Plasma is generated by glow discharge from the needle electrode in a helium
gas stream. The plasma includes ions, electrons, and excited state (metastable)
atoms or molecules. The majority of charged particles are eliminated by the
grounded electrode and the excited state neutral species are expelled to the
atmosphere.
The gas stream can be heated by the gas heater to help analytes
vaporization or desorption from the substrate surface.
Positive ion
The metastable helium atoms formed in the DART source react with
atmospheric water to produce ionized water clusters. These protonated water
clusters can then react with the analyte (M) to form protonated cations:
He(23S) + H2O → H2O+. + He(11S) + e-
H2O+. + H2O → H3O+ + OH.
H3O+ + nH2O → [(H2O)n+1 + H]+
[(H2O)n+1 + H]+ + M → [M + H]+ + (n+1)H2O
Negative ion
Metastable helium atoms can react with a neutral (N), such as the exit grid
electrode, or another neutral species to form electrons through Penning
ionization. The electrons formed are rapidly thermalized by collisions with
atmospheric gases (G) and then react with gaseous oxygen to produce oxygen
anions.
He(23S) + N → N+. + He(11S) + e-*
e-* + G → G* + e-
e- + O2 → O2-
These oxygen anions can then react with sample molecules (M) to produce
analyte anions.
O2-. + M → [M - H]- + OOH.
O2-. + M → M-. + O2
O2-. + M → [M + O2]-.

|
Subjects for analysis
|
Paper (bills, business cards, etc.), film, textiles, fruits, vegetables, spices, beverages, biofluids, human skin, glass, concrete, etc.
|
Detectable
components
|
Drugs and their metabolites, synthetic chemicals, dyes, pigments, pesticide, odor components, narcotics, designer drugs, chemical warfare agents and related substances, explosives, etc.
|
Information update ...